How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and this guide provides a comprehensive answer. From pre-flight checks and understanding your drone’s controls to mastering flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage, we’ll cover everything you need to know to become a confident and responsible drone pilot. We will explore the intricacies of navigation, photography, and legal compliance, equipping you with the knowledge to safely and effectively operate your drone.
This guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, starting with essential safety procedures and progressing to more advanced techniques. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this resource offers valuable insights and practical advice to help you take to the skies with confidence and responsibility.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all the essentials, including practical tips and safety procedures, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components and systems to identify potential issues that could lead to accidents or malfunctions. Neglecting this step can result in significant damage to the drone, property, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight inspections are paramount for mitigating risks associated with drone operation. They allow for early detection of problems like low battery levels, damaged propellers, or faulty GPS signals, preventing potential mid-flight failures.
Comprehensive Pre-Flight Checklist, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive checklist should be followed before every flight. This checklist ensures all critical components are functioning correctly and helps maintain the drone’s overall operational integrity.
| Checklist Item | Inspection Method | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Visual inspection of battery indicator | Above 20% charge (ideally 80%+ for longer flights) | Below 20% charge; visible damage to battery |
| Propeller Inspection | Visual and tactile inspection | No cracks, chips, or significant wear; securely attached | Cracks, chips, or significant wear; loose or damaged propellers |
| GPS Signal | Check GPS indicator on the controller | Solid GPS signal with sufficient satellites locked | Weak or no GPS signal; multiple satellites not locked |
| Gimbal Calibration | Check gimbal movement and stability | Smooth and stable movement; no noticeable wobble | Gimbal is jerky, unstable, or makes unusual noises |
| Radio Control Connection | Check the connection between the drone and controller | Stable connection with full signal strength | Intermittent connection or low signal strength |
| Flight Environment Check | Observe surroundings for obstacles and potential hazards | Clear airspace, no obstacles, safe landing area identified | Obstacles present; unsafe landing area; strong winds |
Emergency Procedures
In case of a malfunction during flight, immediate and appropriate action is crucial. This might involve initiating an emergency landing procedure or executing a controlled descent. Familiarization with the drone’s emergency features and having a practiced response is essential.
- Immediately switch to Return-to-Home (RTH) mode if available.
- If RTH fails, attempt a controlled descent, prioritizing a safe landing area.
- If the drone becomes unresponsive, cut power to the drone using the emergency stop switch (if equipped).
- Assess the situation after landing and determine the cause of the malfunction.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes

Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios, allowing for both precise control and more adventurous maneuvers.
Drone Control Calibration
Calibration ensures the drone’s controls respond accurately and consistently. This process typically involves centering the sticks and aligning the sensors. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions as they vary between models.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to enter calibration mode (usually involves holding specific buttons or stick combinations).
- Carefully follow on-screen prompts or instructions in the manual.
- Once calibration is complete, test the controls to ensure proper responsiveness.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer multiple flight modes, each designed for different skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for faster, more agile maneuvers.
- Beginner Mode: Restricted speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Increased speed and responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for positioning and stability, facilitating easier navigation.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of its position.
Control Stick/Button Functionalities
The control sticks and buttons on your remote controller govern various aspects of the drone’s flight. Understanding their functions is crucial for effective control.
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude (vertical movement).
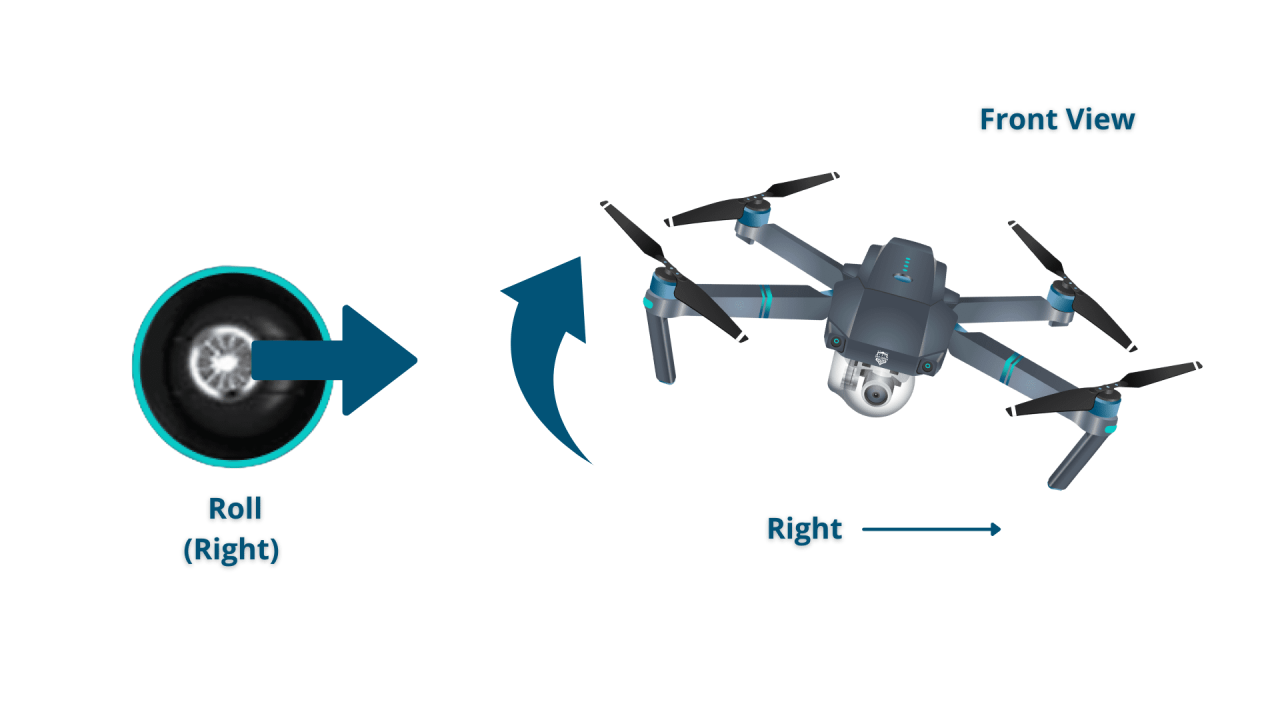
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the motors, immediately stopping the drone’s movement.
Takeoff and Landing Sequence
A consistent takeoff and landing procedure ensures safe operations. This flowchart illustrates a typical sequence.
(Flowchart would be visually represented here, but as per instructions, textual description is provided.)
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Verify GPS signal lock.
- Calibrate the drone (if necessary).
- Check the battery level.
- Slowly lift off the drone using the throttle stick.
- Hover for a moment to check stability.
- Perform the desired flight maneuvers.
- Slowly lower the drone using the throttle stick for landing.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Navigation and Flight Techniques
Effective drone navigation combines understanding the drone’s controls with using available tools and techniques. This ensures safe and controlled flights, particularly in challenging environments.
Drone Maneuvering Techniques
Mastering various maneuvering techniques is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This includes precise control of altitude, direction, and speed.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Precise Movements: Making small, controlled adjustments to the drone’s position.
- Turning: Rotating the drone smoothly and accurately.
- Forward/Backward/Sideways Flight: Moving the drone in specific directions.
GPS and Visual Navigation
GPS and visual cues work together to provide accurate positioning and orientation during flight. GPS provides positional data, while visual cues help maintain situational awareness and avoid obstacles.
- GPS: Provides precise location data for navigation and return-to-home functions.
- Visual Cues: Using landmarks and visual references to maintain orientation and avoid obstacles.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often make mistakes that can lead to accidents or poor flight performance. Understanding these common errors helps prevent them.
- Ignoring pre-flight checks: Leads to potential malfunctions during flight.
- Flying in strong winds: Can result in loss of control.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Risks collisions.
- Not understanding the drone’s limitations: Leads to exceeding its capabilities.
Flight Path Planning and Execution
Planning a flight path before takeoff helps ensure a safe and efficient flight. This involves considering the drone’s capabilities, the environment, and the desired shots.
- Identify the starting and ending points of the flight.
- Consider the route and potential obstacles.
- Visualize the shots and plan camera movements accordingly.
- Execute the flight path, making adjustments as needed.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality images and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and employing effective photography and videography techniques. This section will explore these aspects.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. Experimentation and understanding the interplay between these settings is key.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the camera sensor to light. Lower ISO values result in less noise but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) allows more light and creates a shallower depth of field.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes offer various creative options for capturing images and videos.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Creates a time-lapse sequence by capturing images at set intervals.
Shot Composition and Visual Effects
Effective shot composition and the use of visual effects can significantly enhance the quality of your drone footage. Understanding principles like the rule of thirds and leading lines can elevate your work.
- Rule of Thirds: Placing key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Using lines within the frame to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Utilizing repeating elements to create visually appealing shots.
Essential Photography/Videography Terms
Familiarizing yourself with common terms will enhance your understanding and control over your drone’s camera.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Aperture | The size of the opening in the lens that lets light in. |
| Shutter Speed | The length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. |
| ISO | A measure of the camera’s sensitivity to light. |
| White Balance | Adjusting the colors in the image to appear natural. |
| Depth of Field | The area of the image that is in sharp focus. |
Battery Management and Charging: How To Operate A Drone
Proper battery care is crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone’s batteries. This involves safe charging practices, correct storage, and understanding different battery types.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
Neglecting proper battery care can lead to reduced flight times, battery failure, and even safety hazards. Following recommended procedures ensures optimal battery performance and longevity.
Charging Process and Safety Precautions
Always charge your drone batteries using the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended during charging.
- Use only the manufacturer-approved charger.
- Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area.
- Never leave batteries charging unattended.
- Do not overcharge batteries.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials.
Battery Storage
Proper storage helps maintain battery health and prevents premature degradation. Store batteries at a moderate charge level (around 30-50%) in a cool, dry place.
Battery Types and Characteristics
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are commonly used in drones, known for their high energy density but requiring careful handling.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): High energy density, lightweight, but require careful handling due to flammability.
- LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate): Safer than LiPo, longer lifespan, but lower energy density.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires adherence to various laws and regulations. These regulations vary by region and are designed to ensure safe and responsible drone use.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Before flying, familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations regarding drone operation. These may include registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses to operate a drone legally. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Certain airspace areas are restricted for drone operation. These include airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Failing to comply can result in penalties.
Summary of Key Regulations
The following table summarizes some key regulations (replace with your region’s specific regulations).
| Regulation | Description |
|---|---|
| Registration | May be required for drones above a certain weight. |
| Airspace Restrictions | Prohibits flying near airports, military bases, etc. |
| Operational Limits | May restrict flight altitude, distance from the operator, etc. |
| Privacy Concerns | Regulations regarding data collection and privacy. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their troubleshooting steps is essential for maintaining operational readiness. Regular maintenance also plays a vital role in preventing issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Several issues can arise during drone operation. Knowing how to identify and address these problems can save time and prevent further damage.
- Low Battery
- GPS Signal Loss
- Motor Failure
- Controller Issues
- Gimbal Malfunction
Troubleshooting Steps
A systematic approach to troubleshooting helps pinpoint the problem and find a solution quickly.
- Low Battery: Land immediately, charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage, consider repair or replacement.
- Controller Issues: Check battery level, try re-pairing the controller.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal, check for physical damage.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing malfunctions and extending the lifespan of your drone. This includes cleaning, inspecting components, and performing firmware updates.
Troubleshooting Guide

This guide provides a summarized troubleshooting approach.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Learning how to maneuver the drone effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. This includes understanding flight modes, battery management, and emergency procedures, all essential for safe and responsible drone operation.
- Identify the problem.
- Consult the drone’s manual.
- Check for obvious causes (e.g., low battery, loose connections).
- Try basic troubleshooting steps.
- If the problem persists, contact support or seek professional assistance.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and a strong commitment to safety. This guide has provided a foundation for your journey, covering everything from pre-flight checklists and control calibration to advanced flight maneuvers and legal considerations. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Embrace the challenge, explore the possibilities, and safely enjoy the thrill of flight.
Essential FAQs
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, temperature). Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single battery charge for most consumer drones.
How do I know if my drone’s GPS signal is strong enough?
Most drones will display the GPS signal strength on their control app. Look for a strong signal indication (usually bars or a percentage) before attempting flight. A weak or no signal will often prevent takeoff.
What should I do if my drone loses signal mid-flight?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back, prioritizing a safe landing area.
Can I fly my drone anywhere I want?
No. Drone operation is heavily regulated. Check local laws and regulations, be aware of airspace restrictions (airports, no-fly zones), and always respect private property.
